Singapore F1 Grand Prix Gets into Green Gear
Singapore Formula 1 Grand Prix is kicking climate action into higher gear. The event will last three days leading up to the 61-lap race on the evening of 2 Oct 2022.
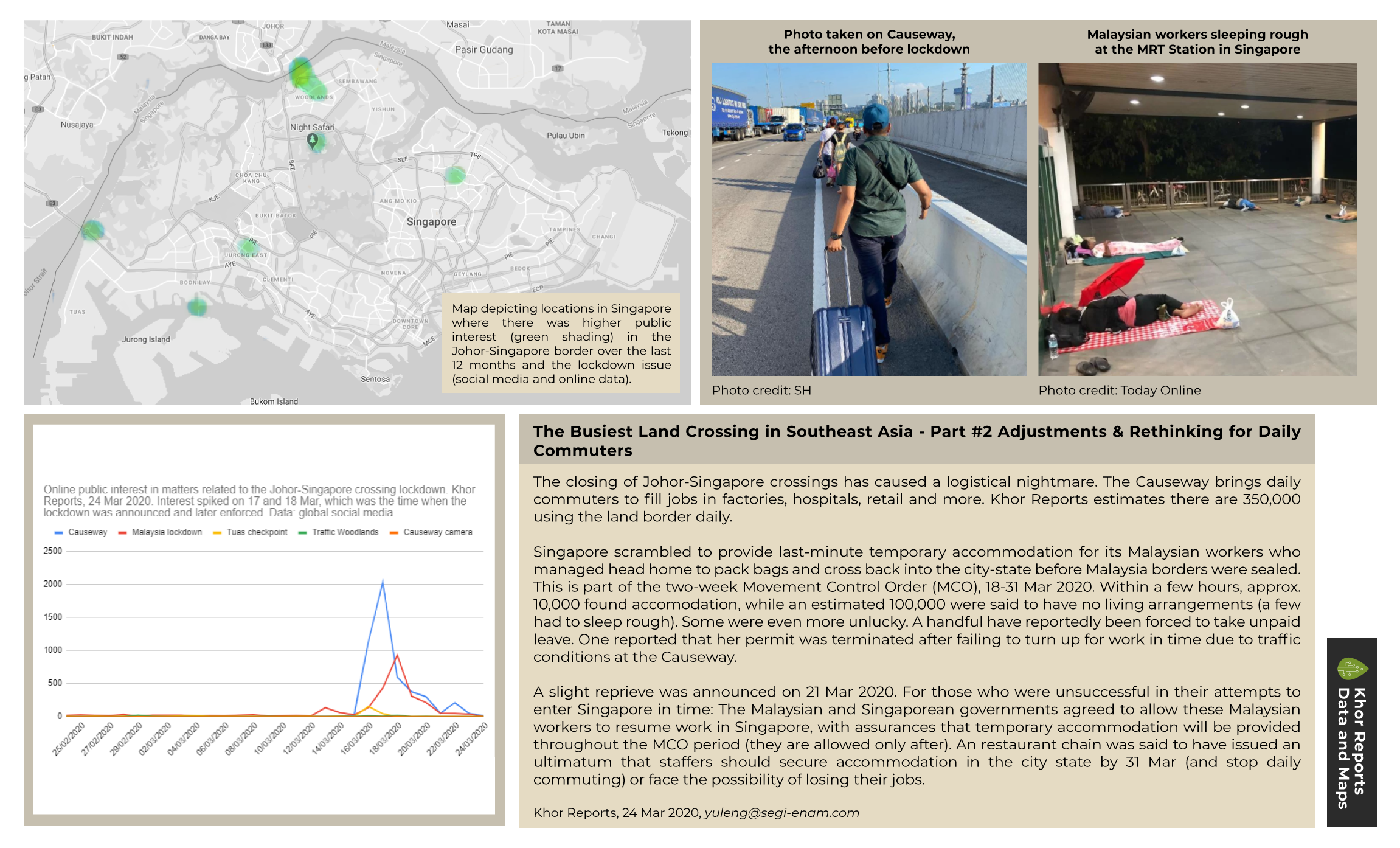
According to a media statement by Singaporean-based biofuels company Alpha Biofuels, “when the night race returns to the streets of Marina Bay in September—after a two-year hiatus due to the pandemic—a full sustainability audit will also be conducted, which could see data such as the amount of carbon emissions and waste generated by the event being measured and reported for the first time.”
Responding to CNA’s queries, a spokesperson from Singapore GP said that the existing track lighting will be replaced with more energy-efficient LED lights from 2023, and that it will switch to electric or hybrid support vehicles where applicable.
The official Singapore Grand Prix website confirms that management consultancy Faithful + Gould has been appointed to write a Carbon Footprinting Report identifying emission sources of concern. The results will be then audited by Tüv Süd PSB.
On that note, take a look at F1’s 2026 target for 100% sustainable fuel and how ARAMCO creates F1’s sustainable fuel. Also significant is Singapore’s import of renewable (hydro-powered) energy from Laos, its challenges, and questions on large-scale dams.
See below for the sustainability commitments listed on the Singapore Grand Prix website:
Source: Singapore Grand Prix (accessed 26 Sep 2022)
research@segi-enam.com | 30 Sep 2022